其他品牌 品牌
代理商厂商性质
北京市所在地

是Flocel公司生产和销售的一个更实际的、动态的体外血脑屏障(DIV-BBB™)模型,更准确地反映真正的血脑屏障特性。
迄今为止,研究者已经使用静态BBB模型或动物模型进行了测试。和这些方法对比,flocel的DIV-BBB模型的优势:
更的药代动力学和毒理学研究
● 更准确地反映体内血脑屏障特性
● 模仿重要的内皮细胞-星形胶质细胞相互作用
● 电测量血脑屏障的完整性
● 能使用真实的人体细胞
● 形成比现有静态模型更紧密的连接
● 可大幅降低药物开发成本

Flocel系统包括测量软件、体外细胞培养组件安装平台、连接电线、四个体外细胞培养组件。盒中的电极插入平台中的匹配连接器。
●腔室内外体积比例可调控
●体积小,仅约7厘米长
●电极固定于装置内
●费用低
●匹配体内的体积比
●减少所需的细胞数量
●电阻容易测量
●一次性使用,不重新安装墨盒

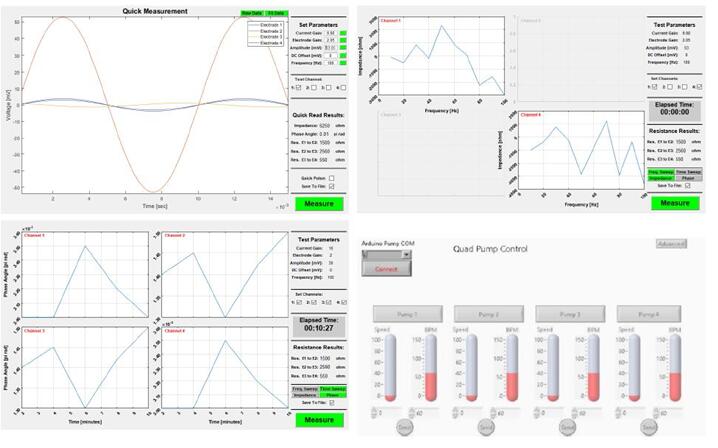
跨内皮电阻(TEER)测定为血脑屏障的完整性提供了一个快速简捷的评价模型。该动态体外血脑屏障模型有与体内血脑屏障相近的跨内皮电阻,可达到>1000 Ω-cm2, 而与之相对,单层模型通常只有<200 Ω-cm2。
特点
●跨内皮电阻测定范围:>1000 Ω-cm2
●可在多重频率下测定阻抗
●低电压设定:大60mV
●可对4个装置进行自动多重处理
●USB接口
●表征血脑屏障的电阻和电容。
●限制对BBB的潜在电压破坏
●能处理多达4个墨盒
●可以使用台式机或笔记本电脑。

Flocel为四个体外细胞培养组件提供了一个小的,很容易配置的蠕动泵,每个泵分别独立控制,允许进行四个独立实验。
热点:
●四个装置中的流速和泵速各自独立控制
●外接24V直流电插入式电源供应
●接收TEER测定系统的程序指令
●允许四个体外细胞培养组件独立控制
●将培养体系内的发热小化
●不需要额外的USB接口
Flocel系统用户通过系统自带的DIV-BBB 2软件包进行操作,为TEER和蠕动泵的测试参数的动态修改提供了一个直观的界面。TEER用户界面显示了原始数据输出、频率、时间等参数选择。蠕动泵的用户界面通过允许每个独立的泵头选择流速和不同的正旋波形,简化了设置四个流体灌注通道的任务。
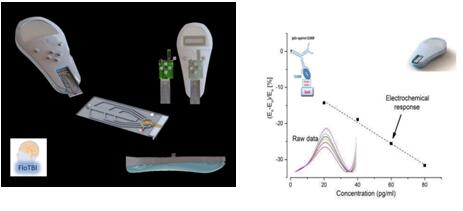
世联博研和Flocel Inc.联合,提供以合同为基础的体外 BBB渗透性测试。费用结构由待测化合物的数量和测试的复杂性决定。这项服务在克利夫兰基金会,斯坦福大学和欧洲的实验室进行。我们还提供脑生物标志物的咨询服务和测试仪器,并通过分析外周血检测人体受试者血脑屏障的完整性,提供诊断患者或运动员血脑屏障的方法。
轻型颅脑损伤(MHI和MTBI)占颅脑损伤的95%;诊断和早期管理包括计算机断层扫描(CT)或住院观察,但是这些选项都不理想。在医院观察是不经济的;CT有时是不切实际的,涉及潜在的有害电离辐射。GFAP和S100等脑蛋白在体液中表达水平与许多神经系统疾病有关联性。Flocel开发了商业化的血液测试小型工具,给创伤性脑损伤进行前期及时诊断,防止严重的延迟性后果。
The role of shear stress in blood-brain barrier endothelial physiology.
Cucullo L, Hossain M, Puvenna V, Marchi N, Janigro D.
A dynamic in vitro BBB model for the study of immune cell trafficking into the central nervous system.
Cucullo L, Marchi N, Hossain M, Janigro D.
Pattern of P450 expression at the human blood-brain barrier: roles of epileptic condition and laminar flow.
Ghosh C, Gonzalez-Martinez J, Hossain M, Cucullo L, Fazio V, Janigro D, Marchi N.
Tobacco smoke: a critical etiological factor for vascular impairment at the blood-brain barrier.
Hossain M, Sathe T, Fazio V, Mazzone P, Weksler B, Janigro D, Rapp E, Cucullo L.
Immortalized human brain endothelial cells and flow-based vascular modeling: a marriage of convenience for rational neurovascular studies.
Cucullo L, Couraud PO, Weksler B, Romero IA, Hossain M, Rapp E, Janigro D.
Side by side comparison between dynamic versus static models of blood-brain barrier in vitro: a permeability study.
Santaguida S, Janigro D, Hossain M, Oby E, Rapp E, Cucullo L.
Glycerophosphoinositol and dexamethasone improve transendothelial electrical resistance in an in vitro study of the blood-brain barrier.
Cucullo L, Hallene K, Dini G, Dal Toso R, Janigro D.
A new dynamic in vitro model for the multidimensional study of astrocyte-endothelial cell interactions at the blood-brain barrier.
Cucullo L, McAllister MS, Kight K, Krizanac-Bengez L, Marroni M, Mayberg MR, Stanness KA, Janigro D.
A Dynamic Humanized drug resistant In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model to assess the permeability of relevant CNS drugs
Development of a novel blood-brain barrier model by coupling Immortalized human brain endothelial cells with flow-based cell culture technologies
Glioblastoma Cell Line Metabolism Under Dynamic and Static Conditions: Effects on tumor growth and BBB integrity
Humanized in vitro blood-brain barrier models to screen for brain penetration of antiepileptic drugs
Effect of Shear stress on BBB endothelial cells: A proteomic study by 2-dimensional protein electrophoresis