品牌
代理商厂商性质
北京市所在地
可以在现实和动态的环境中研究整个炎症途径。通过用内皮细胞管腔重建共培养的组织和/或肿瘤细胞的组织切片,SynVivo平台可在平台上提供包括流动和剪切在内的生理逼真的模型,并能够实时跟踪滚动,粘附和迁移过程。该模型已经成功地针对体内研究进行了验证,该研究显示出与滚动速度,粘附模式和迁移过程具有*的相关性(Lamberti等,2014; Soroush等,2016)。
逼真模拟人体内的血管血流ding尖的微流控技术,用于细胞培养和观察细胞滚动、粘附、迁移的得力助手,可用于观察细胞与细胞、细胞与配体之间的在流体状态下互相作用的新型体外流体动力学平台
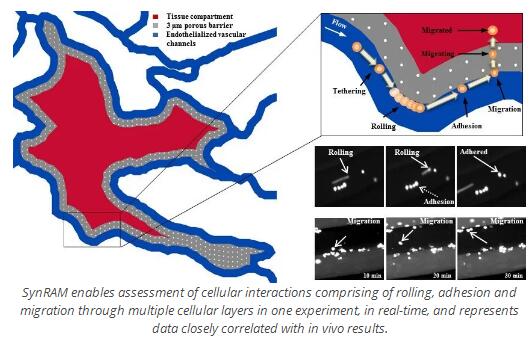
SynRAM能够在一个实验中实时评估细胞相互作用,包括多个细胞层的滚动,粘附和迁移,并代表与体内结果密切相关的数据
SynRAM 3D炎症模型提供了一个现实的测试环境,其中包括:
微血管环境中的生理切应力
具有*封闭腔的体内类血管形态
细胞间相互作用的共培养能力
单个实验的实时定量滚动,粘附和迁移数据
SynRAM能够在一个实验中实时评估细胞相互作用,包括通过多个细胞层的滚动,粘附和迁移,并代表与体内结果密切相关的数据。
SynRAM的创新设计克服了流动室或基于Transwell室的测定法固有的当前局限性。当前的流动室设计过于简单,缺乏微环境的规模和几何形状,无法模拟迁移。同样,Transwell腔室无法解决体内观察到的流体剪切力和尺寸/拓扑结构,迁移的终点测量结果不可重现,并且无法提供实时可视化效果。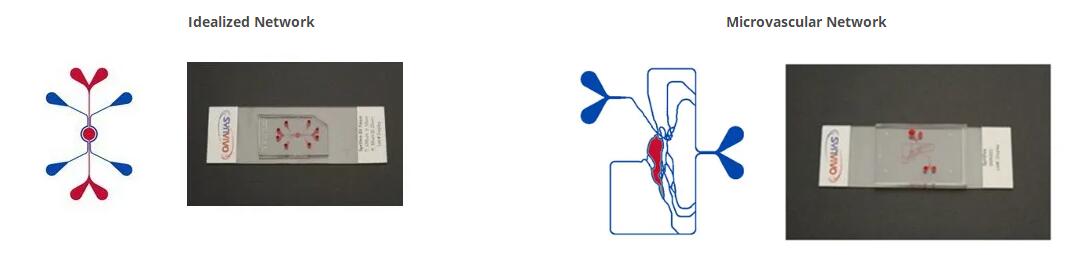
SynVivo的专有芯片设计范围从复杂的体内衍生微血管网络(从数字化图像获得)到产生逼真的细胞组成和血管形态,从而导致剪切和流动条件变化,再到简化的理想化网络,旨在再现细胞组成以及恒定的剪切和流动条件。
SynRAM 3D模型套件组件
可以以试剂盒形式购买使用SynRAM模型进行测定所需的所有基本组件。 根据个人研究需求,您可以从SynRAM芯片的“理想化”或“微血管”配置中进行选择。 包括所有附件,包括管子,夹子,针头和注射器。 入门工具包还将包括气动启动装置(使用SynRAM进行分析需要)。 套件内容和说明
Kits include the following components:
| SynRAM | Assay Kit- Idealized or Microvascular Cat#s 401001, 401003 | Starter Kit-Idealized or Microvascular Cat#s 401002, 401004 |
| 102008-SR (Idealized) or 105001-SR (Microvascular) Chips (10) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Pneumatic Primer and Adapter | ✓ | |
| Manifold (5 ports) | ✓ | |
| Blunt Tip Needles 0.5” long, 24ga (50) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Tygon Tubing 0.2” ID x 0.6” OD(100 ft) | ✓ | ✓ |
| 1 mL Syringes (50) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Slide Clamps (25) | ✓ | ✓ |
SynRAM successfully validated against in vivo data
SynRAM microfluidic chips comprising of realistic microvascular networks were used to understand the role of classical inhibitors of individual steps of the leukocyte adhesion cascade. Experimental results matched very well with in vivo data highlighting the unique ability of the platform for real-time analysis of these dynamic events in a morphologically realistic environment (Lamberti et al 2014).

Neutrophil rolling using SynRAM microfluidic chips is similar to leukocyte rolling in vivo; Box and whisker plots summarizes the comparison of leukocytes rolling velocity measured in vivo and in SynRAM chips and shows no significant difference (p=0.758; Mann-Whitney Rank Sum Test). The “+” marked in the box indicates the mean.

Neutrophil adhesion in SynRAM microfluidic chips is similar to leukocyte adhesion in vivo; Distribution of the number of adhered leukocytes and neutrophils as a function of distance from the nearest bifurcation in vivo in mouse cremaster muscle model and in vitro in microfluidic chips, respectively. Both histograms are skewed to the left indicating that leukocytes and neutrophils preferentially adhere near bifurcations with the peak occurring at one vessel or channel diameter from the nearest bifurcation.
Bioinspired Microfluidic Assay for In Vitro Modeling of Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions. G. Lamberti, B. Prabhakarpandian, C. Garson, A. Smith, K. Pant, B. Wang, and M.F. Kiani. Anal. Chem., 2014, 86 (16), pp 8344–8351 DOI:10.1021/ac5018716
Investigation of the Effect of Blocking of Specific Steps of the Inflammation Pathway using Monoclonal Antibodies
Antibody blocking of specific steps in the adhesion/migration cascade downregulates other steps of the cascade; Monoclonal antibodies against E-selectin (aE-selectin), ICAM-1(aICAM-1), and PI3K (wortmannin) significantly reduced the number of rolling, adhering, and migrating neutrophils in SynRAM microfluidic devices.

Percent activity after treating cells with the respective antibody blockers in comparison to their corresponding control values.
Elucidation of the Mechanism of Protein Kinase C delta (PKCδ) in Sepsis Related Inflammation Response
The SynRAM model was used to identify the underlying mechanism of Protein Kinase C delta (PKCδ) dependent neutrophil-endothelium interactions which has been found to play a significant role in the inflammatory response. Under physiological fluid flow conditions and using the simultaneous real-time monitoring ability of the entire inflammation process comprising of rolling, adhesion and migration, they found PKC𝛿 was a critical regulator of human neutrophil adhesion and migration through human endothelial cells during inflammation.

PKCδ-TAT inhibitor significantly reduces migration of neutrophils from the vascular channels, across the inflammed endothelium (treated with TNF-α for 4 or 24 hour), into the tissue compartment in response to fMLP mediated signaling compared to untreated controls.

Immunohistochemical detection of myeloperoxidase (MPO) in representative lung tissue sections from 24 h post surgery. Few MPO-positive cells in Sham surgery. Sepsis induces the infiltration of numerous MPO-positive cells throughout the lung parenchyma. PKCδ-TAT Inhibitor significantly reduces sepsis-induced, MPO-positive cell numbers in the lung indicating decreased neutrophil migration.